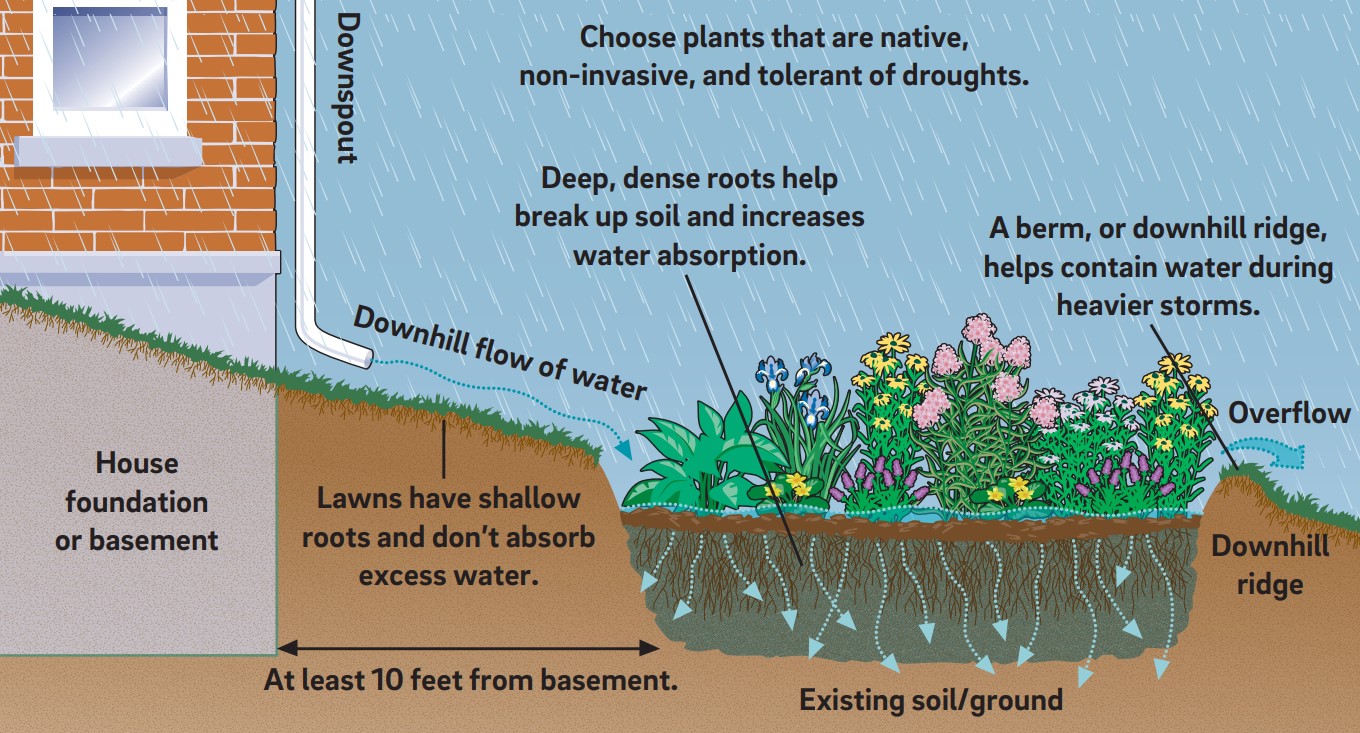
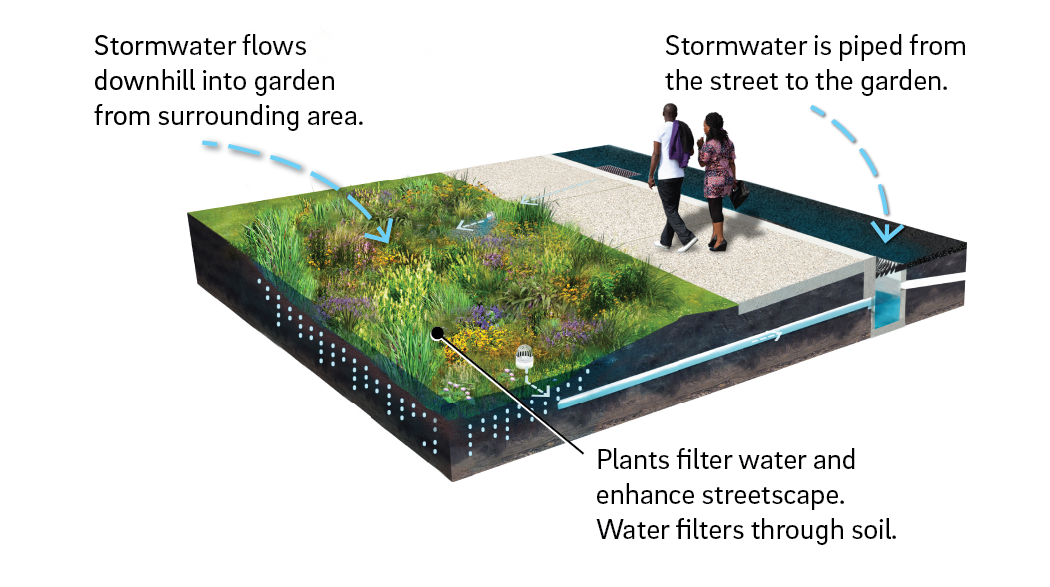
A rain garden is vegetation designed to collect runoff from impervious surfaces, allowing water to infiltrate the ground. Rain garden plants are generally robust native species that can thrive in extremely wet and dry weather.

A rain garden is designed to collect runoff from impervious surfaces such as roofs, walkways, and parking lots, allowing water to infiltrate the ground. The garden is normally lower than the surrounding ground level. The bottom layer is filled with stone, allowing runoff to collect and pond within it. The system is designed to allow stormwater to flow into the rain gardens from nearby impervious areas. After the water ponds on the surface, it’s used by the vegetation in evapotranspiration and infiltrates into the subsurface stone storage and soil. Rain gardens can be connected to sewer systems through an overflow structure, but they are usually sized to infiltrate the collected stormwater runoff within 72 hours. Flexible and easy to incorporate into landscaped areas, rain gardens are suitable for many types and sizes of development and retrofits. Rain gardens are effective at removing pollutants and reducing stormwater runoff volume.